Category Archives: Uncategorized
Does Climate Change Contribute to Violence and War?
Severe droughts can devastate crops and force farmers off their land, sometimes contributing to conflict in already strained regions. While climate events play a role, economic policies, political instability, and other social factors are also key drivers of displacement and unrest.
Read the full article on our website: Does Climate Change Contribute to Violence and War?
Plastic in the Food Chain
Researchers have found that about a quarter of fish sold in California and Indonesia contained plastic or fibers in their guts, linking ocean pollution directly to the food we eat. While it’s unclear how much risk this poses to humans, plastics can carry harmful chemicals that disrupt hormones and attract toxins. Scientists estimate eight million tons of plastic enter the oceans each year — a growing threat to marine life and people alike.
Read the full article on our website: Plastic in the Food Chain
Where Have All the Boys Gone?
Male births are declining worldwide, and scientists are linking it to endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in plastics, pesticides, and fertilizers. These pollutants interfere with hormones, lowering sperm counts and causing reproductive abnormalities in both humans and wildlife.
Read the full article on our website: Where Have All the Boys Gone?
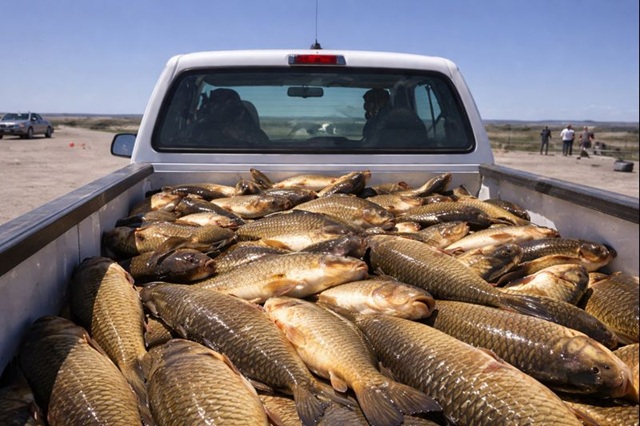
Oregon Food Processor Wants To Turn Invasive Carp into Organic Fertilizer
Malheur Lake in Oregon was once a thriving habitat for migratory birds, producing over 100,000 ducklings annually. But since carp were introduced in the early 1900s, they’ve taken over the lake — uprooting aquatic plants, stirring up sediment, and destroying vital nesting grounds.
Now, a new partnership between the Malheur National Wildlife Refuge and Silver Sage Fisheries and Nutrient Company aims to turn the problem into a solution. The company plans to harvest the invasive carp and process them into organic fertilizer for local farms.
During a trial, over 40,000 pounds of carp were caught, marking the first step in a $500,000 project to restore the lake’s ecosystem while creating a sustainable agricultural product.
Read the full article on our website: Turning Invasive Carp into Fertilizer
DO NOT FEED THE DUCKS!
Feeding ducks may seem like a fun, harmless activity, but it can actually cause serious harm to both the birds and their environment. Bread and other human foods are poor substitutes for natural diets of aquatic plants, grains, and invertebrates. Artificial feeding can lead to inbreeding, overcrowding, delayed migration, disease, deformities, and even water pollution.
Decomposing bread also worsens algae growth, pollutes water, attracts rats, and contributes to foul odors. If you want to feed ducks, choose nutritious options like duck pellets, seedless grapes, shredded leafy greens, or grains such as oats and barley.
Read the full article on our website: Do Not Feed the Ducks!
Where Does All the Road Salt Come From?
In 2013, U.S. officials applied about 17 million tons of salt to roads to melt snow and ice. While it helps keep roads safe, road salt damages metal and concrete, contaminates drinking water, and harms aquatic ecosystems — with up to 70% of it staying within the watershed.
The U.S. is the world’s second-largest salt producer, after China, and imports around 12 million tons annually, mainly from Canada and Chile. Most rock salt originally formed from ancient oceans that have long since evaporated, leaving massive underground salt deposits.
Read the full article on our website: Where Does All the Road Salt Come From?
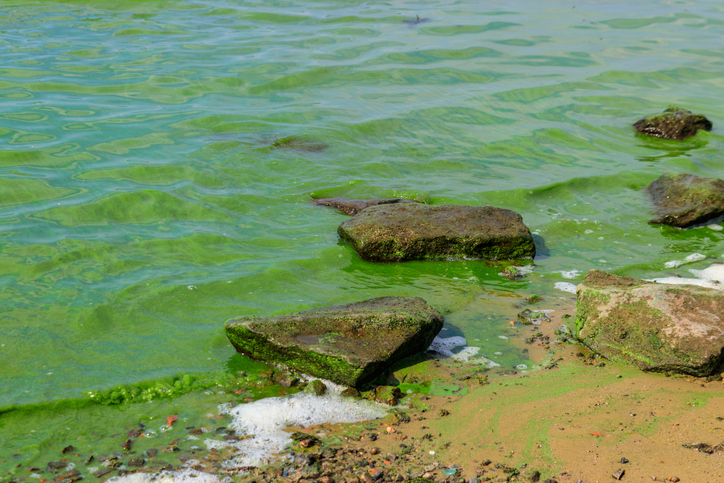
Algae Virus Found in Humans
Scientists from Johns Hopkins and the University of Nebraska discovered a virus — once thought to only infect algae — living in 40% of people tested. Known as ATCV-1, it may affect brain function and processing speed, raising questions about how algae-related viruses interact with humans and animals.
Read the full article on our website: Algae Virus Found in Humans
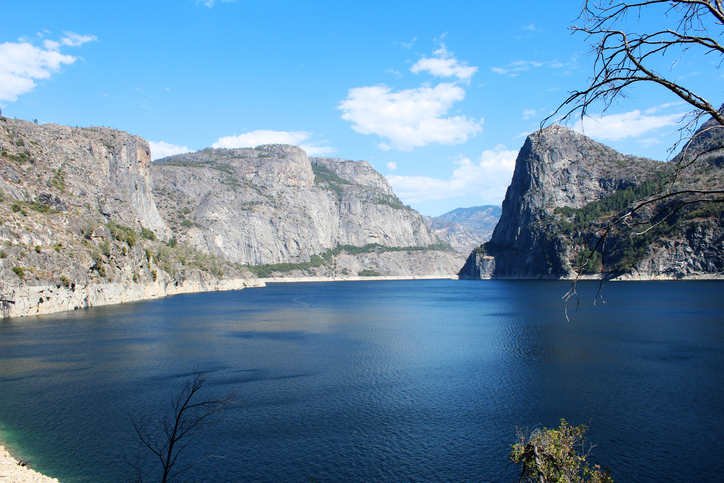
Yosemite Valley’s Twin Sacrificed for Drinking Water
Hetch Hetchy Valley, once nearly identical to Yosemite Valley, now lies underwater beneath the Hetch Hetchy Reservoir. Built after the 1906 San Francisco earthquake to supply clean water and power, the project flooded a once-spectacular glacial valley. Today, it serves over two million people and generates 1.6 billion kilowatt hours of electricity annually—but the debate over whether the dam should remain continues.
Read the full article on our website: Yosemite Valley’s Twin Sacrificed for Drinking Water
$5 billion Revival Leaves the Milwaukee River Cleaner
Thanks to $5 billion in improvements—including the deep tunnel system, dam removals, and phosphorus reduction—the Milwaukee River is cleaner and more valuable than it has been in the past century. Stronger environmental regulations have helped, but questions remain about balancing development with green space and further improving water quality.
Read more: $5 Billion Revival Leaves the Milwaukee River Cleaner